Post-Penguin SEO Link Building: The Naked (URL) Truth
If your rankings haven’t recovered from Google Penguin yet, you’re looking for answers. By now, you’ve cleaned up onsite keyword spam, you’ve stopped participating in blog networks, and you’ve read a ton of articles about how to recover from Penguin, but nothing is working. The fortunate reality is that Penguin is simply an algorithm; a mathematical calculation that factors in different data sets to result in a “score” which is used to rank every Website you see in the search results. The first step to beating this algorithm is to understand it.
The primary method by which Penguin operates is by examining your inbound link profile metrics to detect what it deems to be “unnatural” activity, and the main signal of unnatural activity appears to revolve around anchor text. As such, if you’ve been hit by Penguin, then it’s likely due to an over-optimized inbound link profile, as determined by the distribution ratio of the anchor text in your inbound link profile.
So, what does a Penguin-affected site’s inbound link profile anchor text distribution look like?
Can you guess what anchors are represented by the big pieces of this pie? Exact-match keyword anchor text for money keywords. This is the type of link profile that would have performed extremely well prior to Google Penguin, but it’s deadly post-Penguin since it lacks diversity, as over 75% of its inbound links are divided into 4 separate anchor texts. This is a big signal to Google of link profile manipulation.Here’s what a healthy inbound link profile looks like:
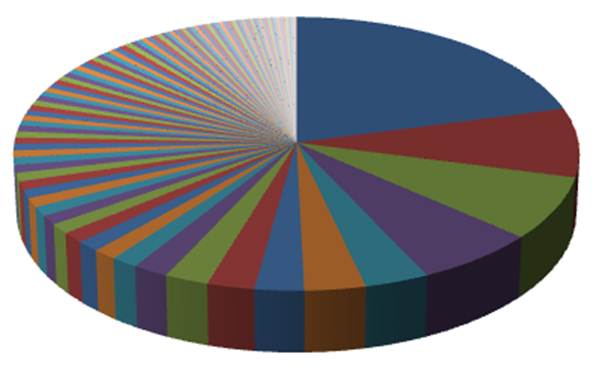
- Naked URLs consist of some variation of the actual URL of the link destination. This can be an internal page or, more commonly, the home page. Naked URLs are the strongest signal to Google of a “natural” inbound link profile and typically comprise the majority percentage of anchor text distribution in healthy websites. Examples include searchenginejournal.com, http://www.searchenginejournal.com, www.searchenginejournal.com, and http://searchenginejournal.com.
- Brand Anchors consist of some variation of the brand name of the destination website. Even small variations such as differences in capitalization are noted by search engines. Examples include Search Engine Journal, SearchEngineJournal, Search engine journal, and SEJ.
- Brand-keyword hybrid anchors consist of some variation of the brand name of the destination website mixed with a relevant exact-match or LSI (latent semantic indexing, which is just a fancy term for “related”) keyword. Examples include SEO blog Search Engine Journal, Search Blog Search Engine Journal, and Search Engine Journal, a search blog.
- Universal/junk anchors consist of words that can apply to any destination website, or are universal in nature, such as “click here,” “visit this website,” and “here.” They are commonly known as “junk” anchors because, prior to Google Penguin, SEOs and webmasters used to try to avoid these types of anchors since they passed no signals of relevance to the destination website. Oh, how the tables have turned.
